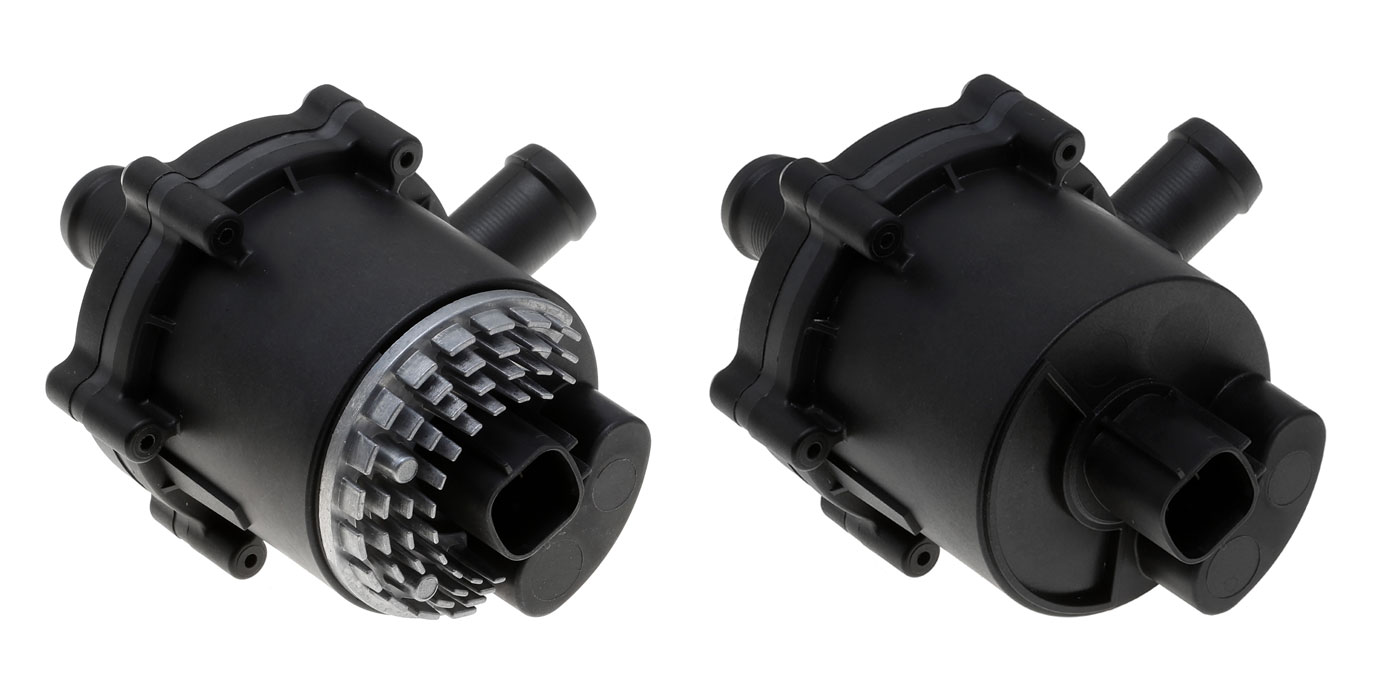
The tiny “bubbles” of water pump cavitation can kill the pump. While you will never actually see the tiny bubbles of cavitation in pumps, you can see the damage of cavitation that looks like metal eaten by termites.
That’s because these are not really bubbles. You see, when it comes to the cavitation in pumps, they are voids. Inside these tiny voids is super-heated vapor that can erode metal and crack plastic. Cavitation in pumps is not typically the fault of the water pump itself; it is only the victim of other problems with the coolant and other components.
The voids of water pump cavitation are generated by the movement of the pump’s impeller against the coolant. There are two types of pressures that determine if cavitation in pumps will occur. The first is the vapor pressure that is related to system pressure. The second is the pressure and suction generated by the pump.
If you remove the radiator cap from a hot system, the coolant is suddenly above its vapor pressure and steam is formed. The same thing can happen inside the water pump. As the impeller spins, its coolant is pushed in one direction and pulled in the other by the blades. If the negative pressure is great enough, voids are formed. Inside the voids is super-heated steam that can cause damage to the impeller and housing.
Coolant Condition and Cavitation In Pumps
The condition of the coolant has a direct relationship to cavitation in pumps. The specific gravity of the coolant depends on the dilution of the coolant with water. If the specific gravity is too high, it will change how the pump operates.
Up to a 70 percent mixture of antifreeze can be used in extremely cold climates to lower the freezing point of the coolant, but the trade-off is reduced cooling efficiency because ethylene glycol carries heat less efficiently. If the concentration of antifreeze to water is too high in hot weather, it may increase the risk of the engine overheating and make cavitation in pumps more likely to occur.
The coolant additive packages contain wetting agents or surfactants that reduce surface tension and allow the coolant to transfer heat more efficiently. Diesel coolant includes additives that prevent water pump cavitation erosion around the cylinder liners.
New coolant includes buffers that can control the pH. Cavitating acidic coolant is even more damaging to plastic composite impellers because the vapor is now acidic.
Water Pump Cavitation Culprits
The health of the overall cooling system can contribute to water pump cavitation. If a system is not able to transfer heat effectively, it will cause hot spots and increase the pressures in the system. Also, leaks in the system can cause cavitation in pumps because the vapor point of the coolant is lower due to the lack of pressure. This is why pressure testing is important.
Restrictions in the system can cause pressure and suction changes that can lead to water pump cavitation problems because of how the coolant flow over the impeller has changed. Restrictions can be caused by a collapsed hose or a clogged radiator. Installing a new water pump on a system with a restriction can limit the life of the new pump.
Signs Of Cavitation In Pumps
There are no outside visual clues of water pump cavitation. The typical symptoms include overheating and possibly leaking from the weep hole of the water pump. In some cases, the impeller will separate from the shaft. It is not until you remove the pump that the full extent of the damage is revealed.
Cavitation in pumps can attack not only the water pump, but also the part of the housing that is contained in the block, front cover or cylinder head. These problems must be addressed if the new pump is going to last.