Sample Review Questions:
1. A thermostat does what?
a. Regulates the operating temperature of the engine
b. Affects the operation of the computerized engine control system
c. Speeds engine warm-up
d. All of the above
2. Counterman A says the water pump pulls coolant from the engine and pumps it to the radiator. Counterman B says leaks from the vent hole or play in the pump shaft are indications that the water pump needs to be replaced. Who is right?
a. Counterman A only
b. Counterman B only
c. Both Counterman A and B
d. Neither one
3. All of the following statements about radiator caps are true EXCEPT:
a. Pressurizing the coolant lowers its freezing temperature.
b. Caps have different pressure ratings.
c. Pressurizing the coolant raises its boiling temperature
d. A weak or leaky radiator cap may cause an engine to overheat.
4. “Premix” antifreeze contains what percentage of water?
a. 25% water
b. 50% water
c. 75% water
d. No water
ANSWER KEY
1D, 2B, 3A, 4B
EXPLANATIONS:
1. The thermostat is a temperature-sensing valve that speeds engine warm-up after a cold start, and regulates the engine’s operating temperature. Temperature control is necessary to reduce emissions and wear, to improve cold driveability and to improve fuel economy.
The thermostat is usually (but not always) located in a housing where the upper radiator hose attaches to the engine. The thermostat blocks the flow of coolant until the engine reaches a certain temperature (typically 195 to 210 degrees). When the thermostat opens, coolant circulates from the engine back to the radiator. If the thermostat fails and sticks shut, it can cause the engine to overheat. If it fails to close, the engine may not reach normal operating temperature.
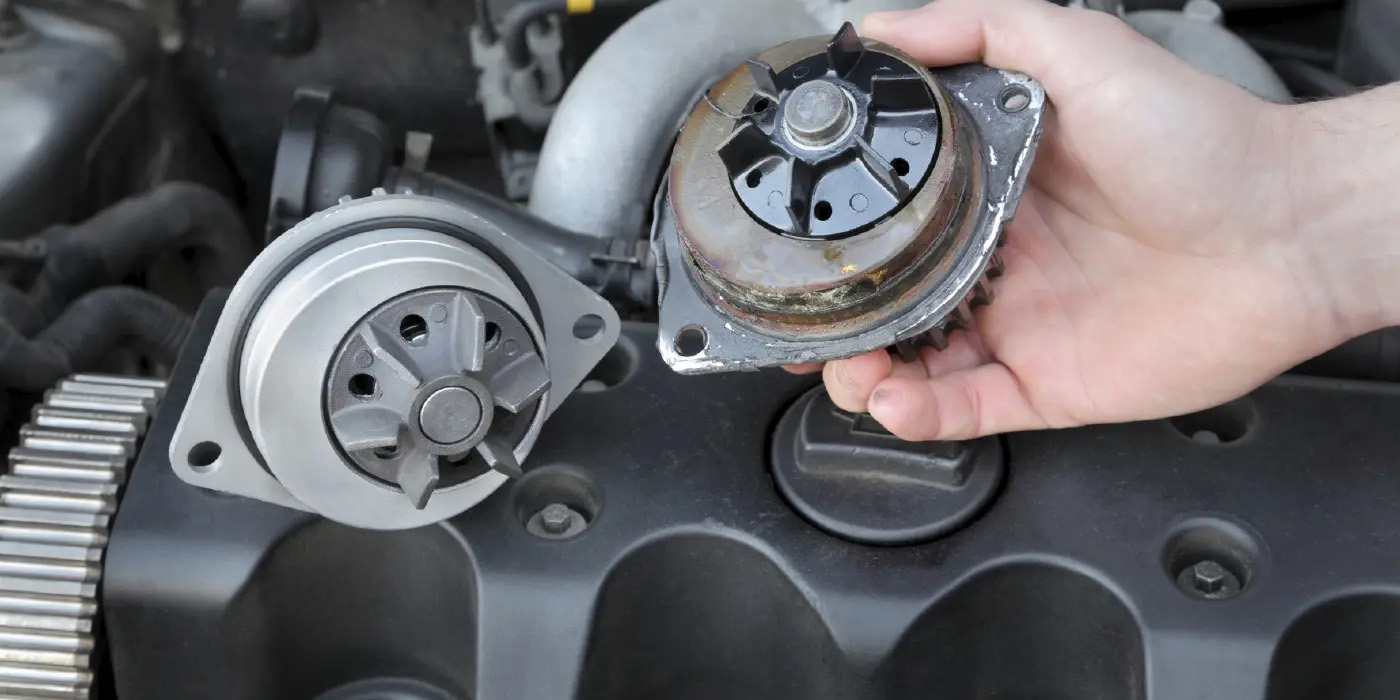
2. The water pump circulates coolant so the engine does not overheat. The water pump pulls coolant from the radiator and pushes it into the engine. When the engine’s thermostat opens, coolant flows back to the radiator and continues to circulate in a loop as long as the thermostat remains open. The water pump has a steel or plastic impeller inside the moves the coolant. The impeller is mounted on a shaft and supported by a ceramic bearing and seal. If the bearing is worn, the shaft may wobble as it rotates causing noise or coolant leaks.
3. A spring-loaded pressurized cap is used on the cooling system to prevent coolant loss and to increase the temperature at which the coolant boils. Pressure ratings are typically 7 to 18 psi. A weak cap that cannot hold its normal pressure can allow coolant loss and overheating. Caps can be pressure-tested to check their performance.
Replacement caps must have the same pressure rating as the original. The radiator cap is usually mounted on the radiator. But on many late-model vehicles, the radiator has no cap, and the cap is mounted on a pressurized coolant reservoir. Others have two caps: a pressure cap on the radiator, and a screw-on filler cap on a non-pressurized coolant reservoir.
4. Automotive cooling systems use a mixture of antifreeze and water. The antifreeze portion provides freezing, boiling and corrosion protection, while water adds increased heat carrying capacity to improve cooling efficiency. The optimum mixture is half water and half antifreeze. With ethylene glycol (EG) antifreeze, a 50/50 mixture will prevent the coolant from freezing down to -34 degrees F and prevent boiling up to 265 degrees F with a 15 psi radiator cap.
Sections covered: