MAJOR COMPONENTS & FUNCTIONS
There are several basic types of ignition systems. Most older engines have distributors, while most newer engines have distributorless ignition systems (DIS), or Coil-On-Plug (COP) or Coil-Near-Plug (CNP) ignition systems
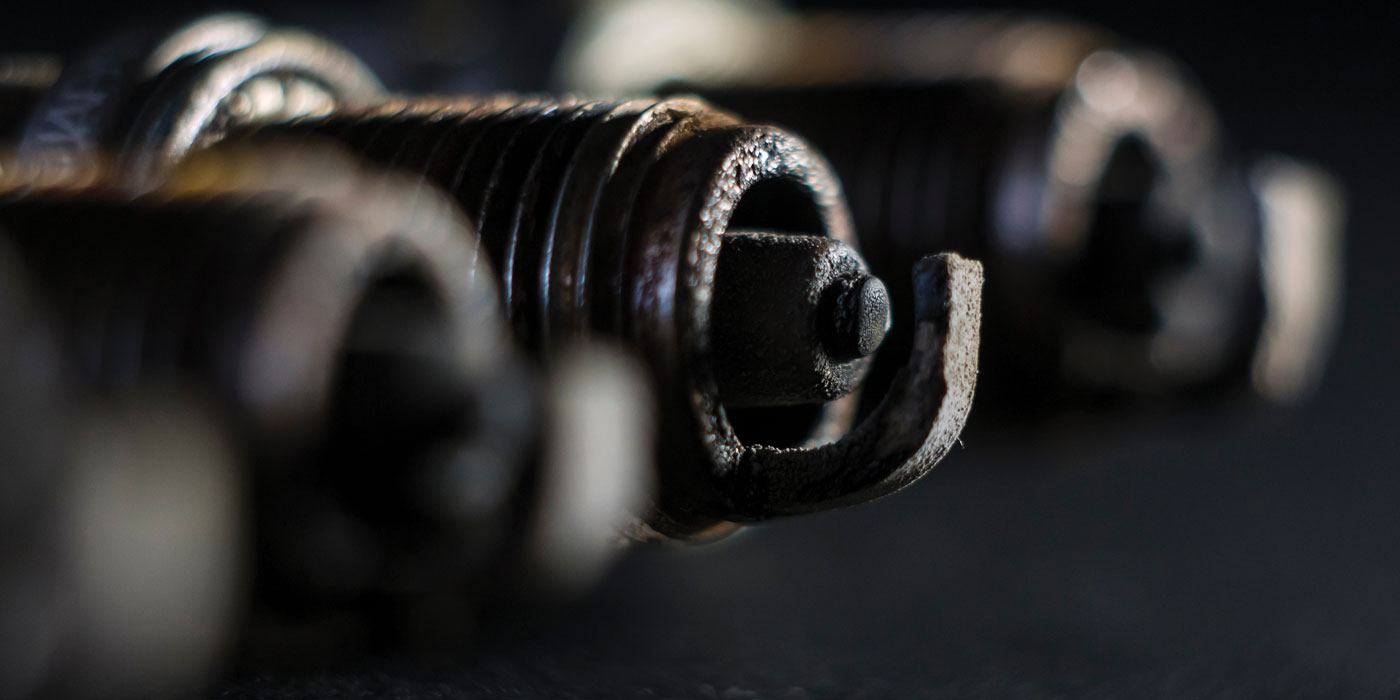
* Spark plugs — Located in the cylinder head, they provide a spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in each combustion chamber. Each spark plug has a ceramic insulator around a conductive core. At the firing end of the plug is an electrode.
A high-voltage spark from the ignition system jumps across the gap to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. Spark plugs have different diameters, thread pitches and lengths depending on the engine application. The “heat range” (operating temperature) of the plugs will also vary depending on the application, as will the electrode gap. Electrode wear and fouling can cause misfiring. Platinum and iridium electrodes are used in long-life plugs to reduce wear and extend plug life to 100,000 miles.
* Spark plug wires — Carry high voltage from the ignition coil(s) to the spark plugs. Ignition cables come in various types (suppression core and inductive or “mag” wire core), with different types of insulation, lengths and diameters (7 and 8 mm). Replacement wire sets must be approximately the length as the original wires. Plug wires may be replaced individually or in complete sets.
Wires must be replaced if the insulation is burned or damaged, or internal resistance exceeds specifications, or the spark plug boots are terminals are loose or damaged.
* Distributor, cap and rotor — Routes high voltage from the ignition coil to the spark plugs. The distributor is mounted on the engine, is driven off the camshaft and rotates at half engine speed. The rotor inside the cap turns to conduct the spark from the center high voltage terminal to each spark plug terminal. The firing order of the wires must be correct, otherwise the engine may backfire or not start. The cap and/or rotor should be replaced if cracked, burned or carbon tracks and arcing are present. Replacing the cap and rotor is also recommended when changing the spark plugs for preventive maintenance.
On older engines, a magnetic or Hall effect pickup is located inside the distributor to generate a timing signal. The signal goes to the “Ignition Module,” which operates the ignition coil.
* Ignition coils — Create high-voltage to fire the spark plugs. On older engines with a distributor, one coil is commonly used (though a few import engines may have two coils). On distributorless ignition applications, there may be one coil per spark plug, or in a “waste spark” DIS system, there is one coil for every two spark plugs (shared spark). Coils run hot and can fail from overheating, causing a weak spark or no spark. On a distributor system, a bad coil may prevent the engine from starting. On a DIS or COP system, a bad coil will cause the affected cylinder(s) to misfire.
* Ignition module — Used in electronic ignitions to control the ignition coil(s). The module has a power transistor that grounds the coil negative terminal to charge up the coil. When the ground is removed, the coil fires and discharges a high-voltage surge to the spark plugs. The ignition module may be mounted inside the distributor cap, on the side of the distributor housing, or located elsewhere in the engine compartment. Modules run hot and can overheat and fail, causing a loss of spark (engine will crank but not start).
* Crankshaft position sensor (CKP) — Generates a timing signal for the ignition system by reading notches in the crankshaft balancer, flywheel or crankshaft. Two types are used: magnetic and Hall effect. Magnetic sensors generate an alternating current (AC) signal that changes in frequency and amplitude with rpm. Hall effect switches produce an on-off digital voltage signal. Loss of the sensor signal will prevent the engine from starting (no spark).
RELATED ITEMS
* Thread repair kits — For stripped spark plug hold threads in cylinder heads.
* Antiseize compound — For spark plug threads.
* Spark plug gapping tool — For checking/adjusting the electrode gap.
INSTALLING IGNITION SYSTEM PARTS
Most spark plugs in late model vehicles have 100,000-mile replacement intervals. Care must be used when changing spark plugs in engines with aluminum heads because the plug threads in the cylinder heads can be easily stripped during removal or installation.
Replacement spark plugs must have the same thread diameter, pitch, length and type of seat as the original spark plugs to fit properly, and should be the same heat range.