The most-often replaced drivetrain components on RWD vehicles are the U-joints. On FWD vehicles, it’s the CV joints. Both are wear components that eventually need to be replaced.
Almost all late-model U-joints are sealed, but some older vehicles have grease fittings for extended life. Some aftermarket replacement U-joints are also available with grease fittings for customers who want them. A worn U-joint may cause vibration at speed, make chirping noises, or produce a clunk when putting the transmission into gear. Replacing a U-joint usually requires using a press to remove and install the joint from the yoke.
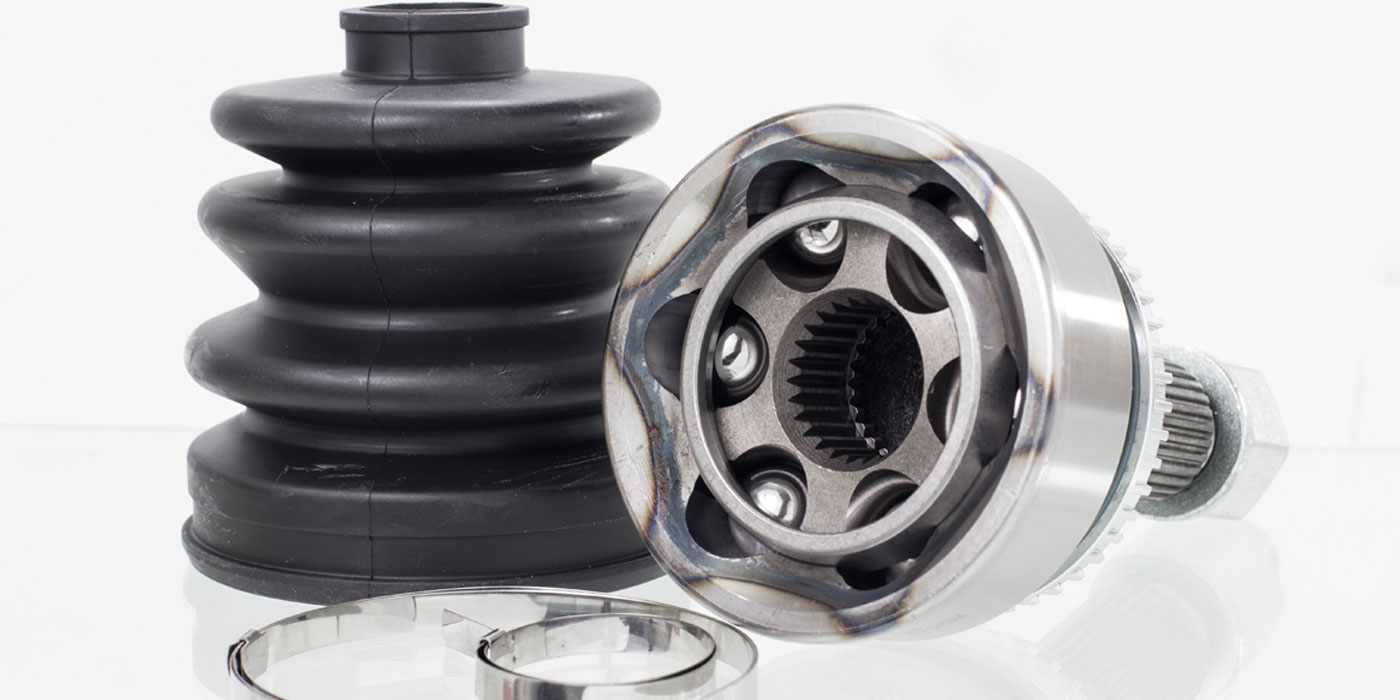
U-joints are not used on front-wheel-drive applications because they can’t handle large operating angles. CV joints are needed for this purpose. Each halfshaft will have a CV joint on each end (one inboard and one outboard). Outboard joints are designed to handle wider operating angles so the wheels can steer, while inboard joints are designed to plunge in and out so the driveline can follow the motions of the suspension.
Basic types of CV joints include Rzeppa, crossgroove, double-offset and tripod. CV joints require special grease that is packed inside the joint and sealed with a protective rubber or plastic boot. Boot damage can allow the loss of grease and joint contamination with dirt or water, leading to joint failure. Damaged boots should be replaced immediately, but are often not discovered until the joint has lost its grease or been contaminated by dirt or water. A typical symptom of a failing CV joint is clicking or popping sounds when turning. Failing inner joints may cause a clunk or vibration when accelerating. CV joints may be replaced separately, or as part of a complete halfshaft assembly. Replacement joints must have the same number of splines as the original, and the same length and diameter input or hub shaft. On vehicles with ABS, there may also be a wheel speed sensor ring on the housing, which must match the original.
The driveline also includes wheel and/or axle bearings at all four wheels to reduce friction. On older vehicles, the bearings are serviceable and require periodic inspection, cleaning and repacking with special wheel bearing grease (never ordinary chassis grease). The components include inner and outer bearings and races, a grease seal and a hub nut, locking ring and cotter pin. A new grease seal and cotter pin should always be installed when the bearings are serviced. Worn or loose wheel bearings can cause steering wander and noise.
The wheel bearings on most newer vehicles are sealed and do not require any maintenance or adjustment. The bearings are part of the hub assembly, which may also include the ABS wheel-speed sensor on some vehicles. On FWD cars, a high-torque hub nut is used to hold the outer CV joint in the hub assembly. Nuts that are staked in place should be replaced if removed to service other parts.
On RWD and 4×4 cars and trucks with solid axles, the outer ends of the axle shafts are supported by bearings located inside the lip of the axle housing. The bearings are lubricated by gear oil in the rear end. Replacement is required if the bearings are making noise, are loose or feel rough when the wheel is spun by hand. Bearings are press-fit on the axle, which requires removing the axle to replace them.
Driveline lubricants include chassis grease for U-joints; CV joint grease for CV joints; wheel bearing grease for wheel bearings; and gear oil for differentials, manual transmissions and transaxles (typically 85W-90, 75W-140, etc.)