This video is sponsored by MAHLE.
In the last video, we talked about the basic types of thermostats, and we mentioned that the automotive industry has been shifting toward newer technology called map-controlled thermostats.
Here’s why: In recent years, automakers have determined that the engine operates best when the coolant temperature is between 200 and 230 degrees Fahrenheit – preferably closer to 230 degrees. However, the automakers feel that a conventional thermostat could allow the coolant to exceed that temperature before circulating coolant through the engine, which could lead to overheating in some situations.
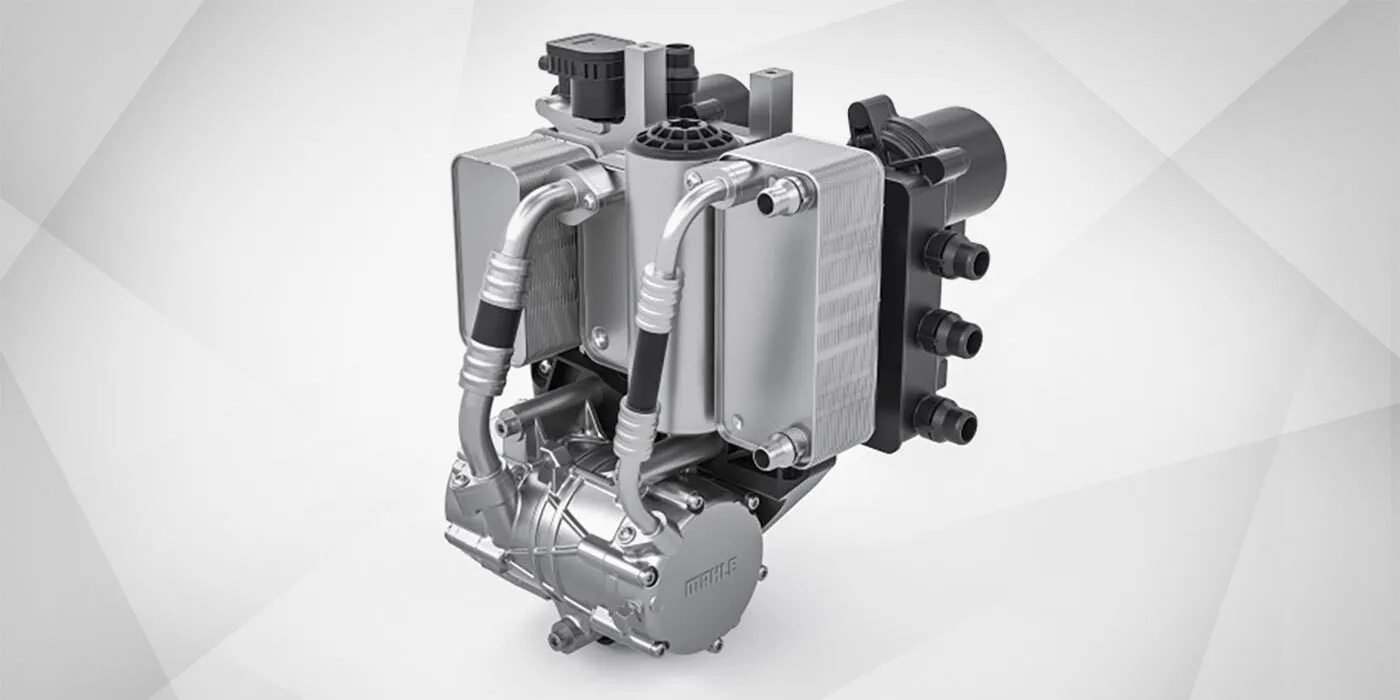
Enter the map-controlled thermostat. This advanced thermostat contains an electric thermal resistor that can heat the wax element inside the thermostat regardless of the coolant temperature, based on signals it receives from the engine control unit.
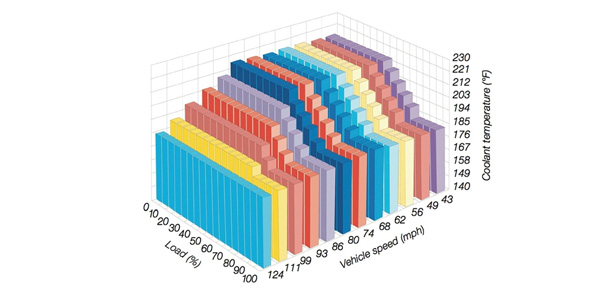
Here’s the cool part: An operating map stored in the engine control unit has predefined set points for the vehicle load and speed that determine the ideal coolant temperature for the driving situation, and when and how coolant should be circulated.
In most everyday driving situations, a map-controlled thermostat will function like a conventional thermostat, circulating coolant when it gets hot enough for the wax to melt and expand. But let’s say the vehicle starts to go up a steep grade, the throttle is opening up quickly and the engine is generating a lot more heat. Because that scenario meets one of the conditions of the stored operating map, the engine control unit will send a signal to the thermal resister to melt the wax element, causing the thermostat to circulate coolant to meet the increased load.
The system is designed for the opposite scenario as well. If a vehicle is driving downhill without using the accelerator, or the ambient temperature drops, the map-controlled thermostat kicks in and lowers the current flow through the heating resistor, or stops it entirely.
By maintaining the ideal coolant temperature, map-controlled thermostats reduce fuel consumption and emissions, improve power output at full load and even make the interior more comfortable in cold weather – which is why we think it’s such a hot topic.