Every single component in a vehicle has a purpose – otherwise, it wouldn’t be there at all. As our vehicles have grown more and more complex, they’ve become more dependent on electrical systems to operate all of the creature comforts to which we’ve grown accustomed. There are hundreds if not thousands of feet of wiring inside today’s vehicles, with dozens of connections throughout.
These electrical circuits, as well as the components that draw power from them, need to be protected in the event of a short circuit or excessive current flow. That’s where fuses come in: They’re the first line of defense for electrical circuits. Fuses are the best (or at least the cheapest) protection we have for electrical circuits.
Fuses and Their Ratings
Fuses are designed to open an electrical circuit if current flow exceeds a given amperage. Inside the fuse is a small wire element that burns away if current flow rises above the rated maximum level. When the element burns away, the circuit is opened, protecting the wires and/or components from literally melting themselves.
The current-flow rating of a fuse is determined by the amount of amperage required to blow the fuse and open the circuit. This rating should be indicated on the fuse body, including a number to indicate the rated amperage followed by the letter “A” for amps. Fuses can easily be replaced, but if there’s an electrical short in the circuit, it will need to be repaired or the replacement fuse will immediately “pop” again.
Whenever replacing a fuse, you always should use the same amperage rating as the one you’re replacing. You never should “upgrade” to a 10A fuse just because the 5A fuse that was there before blew out. Doing so could damage wiring or connectors in the circuit that aren’t designed to handle that level of current flow.
Finding Your Way Around
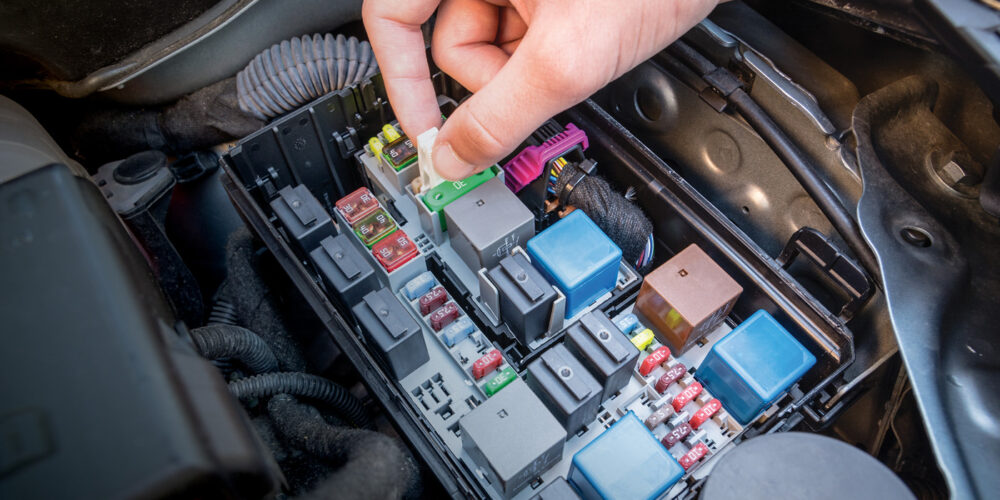
There are a lot of fuses in today’s vehicles, so how do you figure out which one protects the circuit you’re working on? It’s usually a very simple matter of opening up the fuse box and reading the guide on the inside of the lid. Most of the time you’ll also find some sort of plastic fuse-removal tool that can be stored underneath the cover. Of course, needle-nose pliers will work in a pinch as long as you work carefully and don’t squeeze too hard.
The automakers all do a pretty good job of numbering all of the fuses and relays, and printing guides or tables underneath the fuse-box covers or lids. However, if you’re working on a vehicle built by the Ford Motor Co., you’ll need to work a bit harder to get the information you want. Ford tends to number its fuse panels, but the actual circuit descriptions are provided in the owner’s manual. If the manual is no longer present inside the vehicle, then you’ll need to reference the OE service information or a comparable repair manual to get the information you need.
If you need a quick and easy way to test for blown fuses, all you need is a test light. With the ignition key set to “OFF,” touch the test light to the small, exposed conductors on top of each fuse. The test light will light up if power is present, and should light up on both sides of the fuse. Then, repeat this test again with the ignition key turned to the “ON” position, engine “OFF.” Some circuits will only power on when the ignition is turned to the “ON” position.