Turbocharger Overview
With an effort to increase fuel efficiency, maintain performance and reduce emissions, vehicle manufacturers are adding turbocharged engines to their lineups at a significant rate. Over the next five years, the turbo service market will continue to experience substantial growth.
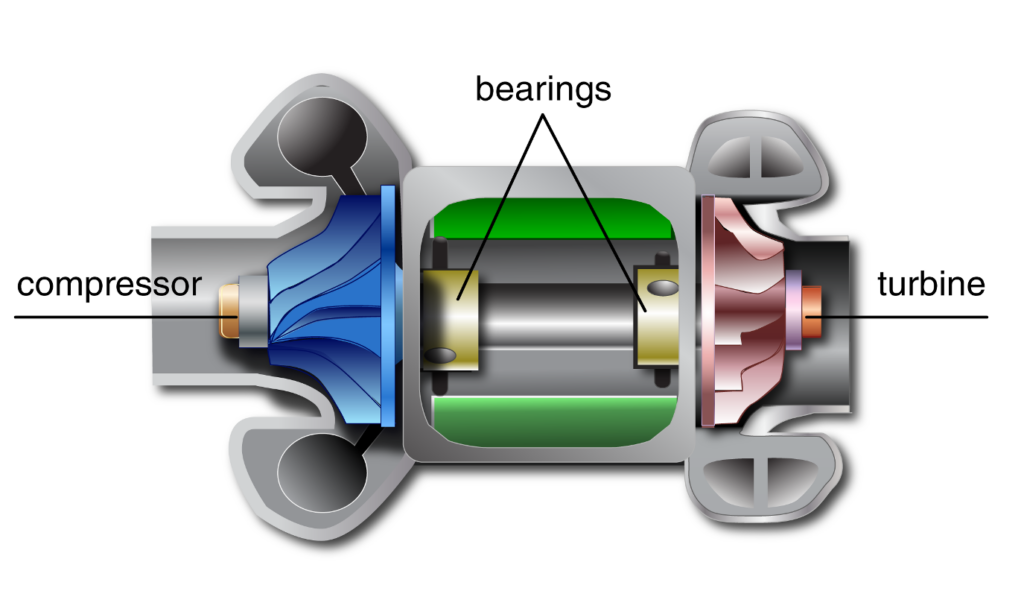
At a basic level, a turbocharger consists of just three major internal components: the turbine, the compressor, and the bearing system that supports the turbine shaft. The compressor wheel, turbine wheel and shaft make up the Center Housing Rotating Assembly (CHRA) which is mounted inside of the turbocharger housing.
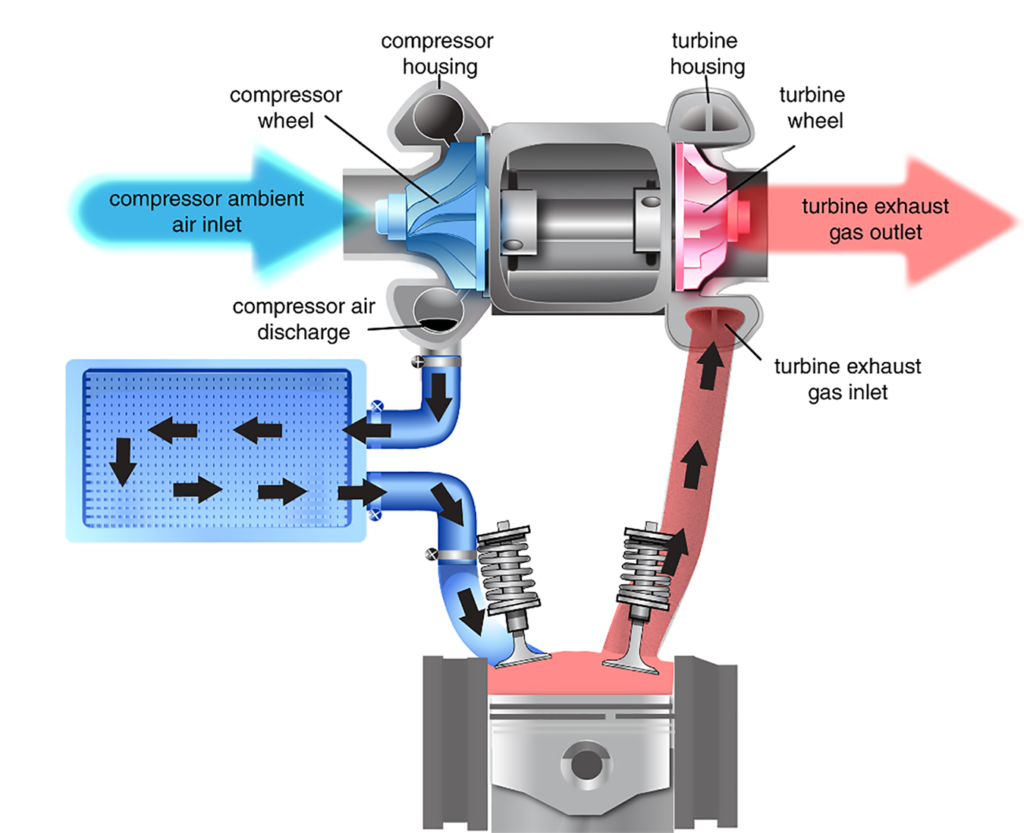
The turbocharger system converts exhaust gases into centrifugal force by flowing the exhaust through the turbine housing forcing the turbine wheel into motion. As the turbine wheel spins, the compressor wheel on the opposite end of the common shaft draws fresh air into the turbocharger, where it is compressed and forced into the intake system. As the intake air is compressed, it builds heat that must be cooled so the air flows through the intercooler before entering the combustion chamber. The result is significantly more air entering the combustion chamber, so more fuel can be added, resulting in better efficiency and more power.
What Causes a Turbocharger to Malfunction?
Symptoms of a malfunctioning turbocharger include loss of power, excess smoke, high fuel consumption, overheating, increased exhaust temperature, and oil leaks from the turbo. It’s important to note that defects in other components can produce the same symptoms. Before mistakenly attributing any of these issues to the turbocharger, remember that turbo performance can be impaired by mechanical damage or blockage caused by debris, or a leak in the turbo ductwork.
If whistling noises (other than normal turbo spooling) are heard coming from under the hood, it’s likely due to boost leaks. The first step is to check all of the joints in the turbo ductwork. Additional attention should be paid to the seams of the intercooler. If the noise persists, check the turbocharger clearances and wheels for housing contact.
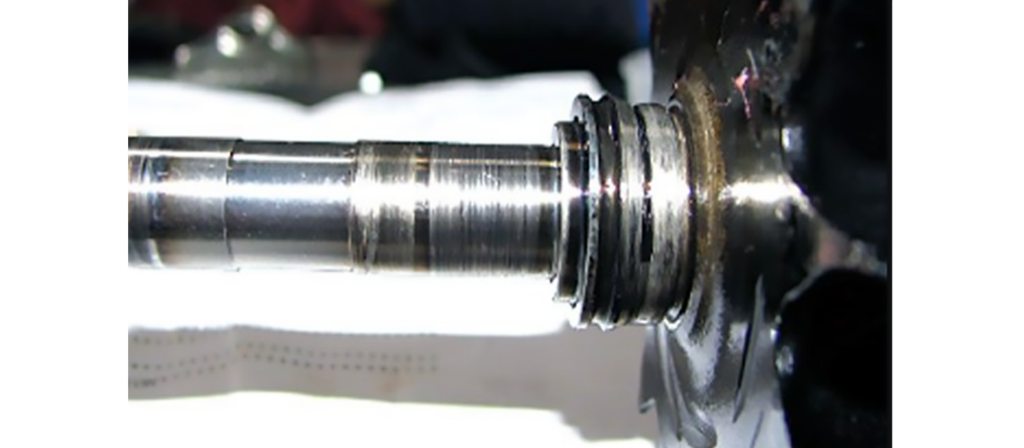

If the turbocharger rotor assembly has seized up or is difficult to rotate, the problem is likely tied to the degradation of the oil. When the oil degrades, it can lead to carbon buildup in the bearing housing interior and can cause the rotor to seize. A turbocharger has specific axial and radial rotor clearances and sometimes, the clearances can be misdiagnosed as worn bearings. Clearances that are out of specification may be associated with a lubricating oil issue. When the turbo is replaced, the technician should always check for insufficient oil, dirt ingress, and oil contamination with coolant.

To determine if the turbo has been damaged by foreign material, inspect the turbine wheel or impeller. If so, there will be clear evidence of foreign material that has entered through the turbine or compressor housings. If the blades are damaged, the turbo needs to be replaced. The technician should inspect for metal that has come off the turbo in the intake tubes. Metal particles in this area may indicate a damaged engine.
Common Trouble Codes
Two typical diagnostic trouble codes for turbos include P0299 (underboost) and P0234 (overboost). If you’re receiving an underboost code, the issue could be a wastegate that’s stuck in the open position or a leak between the compressor and throttle. Causes of overboost, on the other hand, include a wastegate that’s stuck in the closed position, a wastegate vent solenoid that’s stuck in the vent position, or leaking or disconnected control hoses.
Choose the Right Replacement Turbo
If the determination has been made that the turbo is faulty, there are a few things to keep in mind when installing a replacement turbo. First, ensure that the air ductwork is sealed and perfectly clean. Next, confirm there is proper lubrication and cooling at the turbo. The new turbo should have fresh engine oil bled through it before starting the engine. Finally, make certain that a new, quality air filter is installed on the vehicle, along with an oil change and replacement of any applicable breathers.
When selecting a replacement turbocharger, remember that quality matters. Standard® offers a complete line of 100% ALL-NEW (not remanufactured) premium turbochargers. This New, No-Core line provides coverage for gas and diesel, domestic and import applications.
Premium Replacements for a Growing Category
Standard® turbochargers are engineered to ensure each performs with precision for the application it is replacing. All Standard® turbos undergo a full spectrum of quality testing including burst test validation, on-vehicle performance and 100% end-of-line testing through the full RPM range.
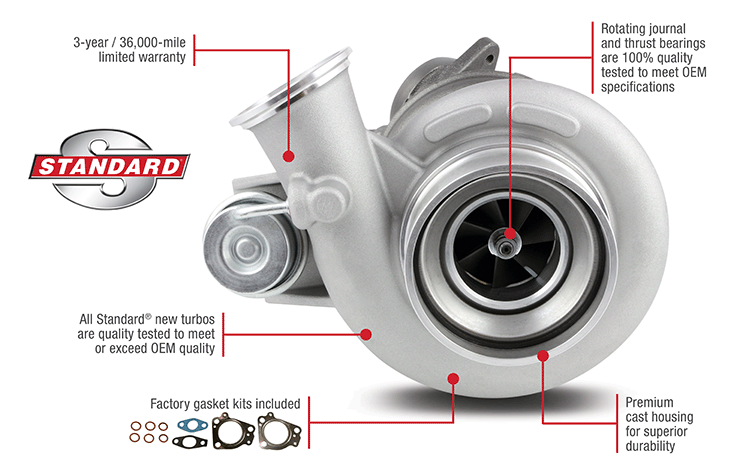
As a quality-plus offering, Standard® new turbo units include factory gasket kits, a 3-year/36,000-mile limited warranty and carry no core charge – that means no core collection, no core inspection, and no core returns. The Standard® line also includes an array of related components – turbo actuators, turbo oil drain tubes, wastegate solenoids, turbo boost, turbo speed sensors and more.
For more information on diagnosing and replacing these components, search “Turbo” on the StandardBrand YouTube channel and to learn about the Standard® Turbo Drop Ship program visit StandardTurbos.com.
















