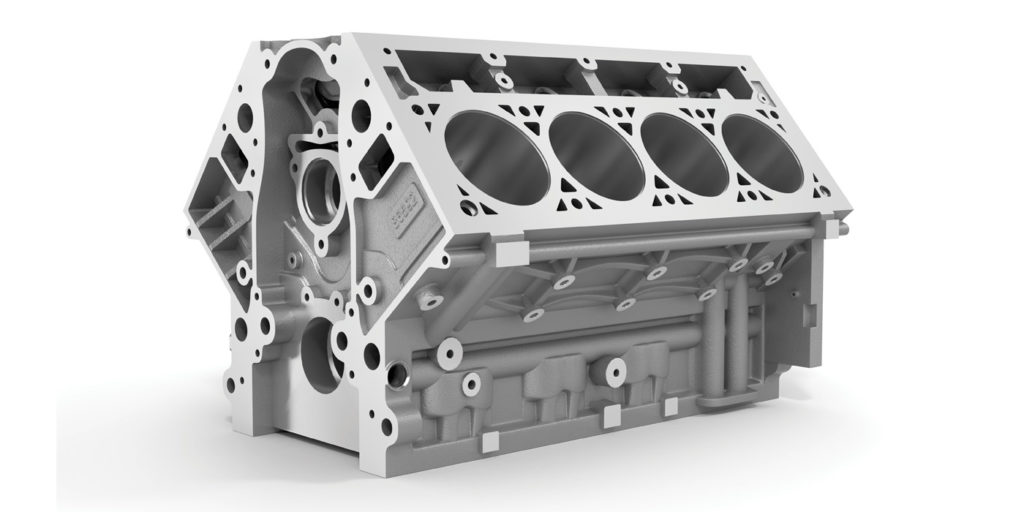
Engine blocks are the core support for all of the rotating parts in the bottom of the engine, including the crankshaft, connecting rods and pistons (and camshaft on OHV engines).
While engines of the past needed a rebuild after 30,000 miles or so (if you took care of it) due to worn bearings and rings, today’s engines can last 200,000 miles or more even without regular maintenance. But when the engine block does fail, it’s usually an expensive repair. Some vehicle owners will forgo engine repairs like this and buy a new or used car instead. But some options won’t break the bank.
A “short block” consists of the cylinder block, crankshaft, pistons and connecting rods for OHC engines, and if it’s a pushrod engine, it also includes a camshaft and timing-chain assembly. Modern engines run tight tolerances between the pistons, piston rings and cylinder walls, so a lack of lubrication can create metal-on-metal contact and generate heat/friction, breaking down the ring seal. Crankshaft bearing clearances also have been reduced in recent years to accommodate thinner oils, making proper maintenance (i.e., oil-and-filter changes) necessary.
If a short block has been destroyed due to overheating or a lack of lubrication or maintenance, one option that counter professionals can offer customers is a remanufactured short-block assembly. If a short-block replacement is done correctly, it can be profitable for jobbers and installers. But if it’s a DIYer undertaking such a complicated repair, it may be best to recommend a complete remanufactured engine instead. Most reman engines come with a warranty and therefore alleviate some of the risk and concern of replacing it.
Because the cylinder block contains the combustion process, there’s a great deal of heat and pressure generated by igniting a mixture of fuel and air to produce an explosion. If the engine has an overheating issue, the heat can cause the cylinder heads to warp or a head gasket to leak. A lack of lubrication can produce enough heat to gall the bearings and snap a connection rod, which could, in turn, break through the side of the block, making a big pile of scrap.
Another problem with cylinder blocks is that it may be porous, which is often the result of a casting defect during the manufacturing process. This affects certain engines more than others, including some older V-8s and import applications. Porosity can lead to leaks and cracks in the block, which can be cold-welded or stitched in some cases. But unless the block is scarce, it’s usually best to replace it.
A cracked block may result in symptoms such as oil and coolant mixing, overheating, low compression or excessive smoke. The cost of repairing a cracked block varies, depending on the shop, the severity of the crack and the application. Used engines are another option, but they are a gamble because you often don’t know the engine’s history or any hidden problems. The technique used to repair the crack also can affect the repair cost, so your customer will have to consider if it’s more cost-effective to buy a new engine or even a new car.